IPRAN Architecture for ISPs
- January 30, 2024
- Posted by: Lyfey Technologies
- Category: Networking
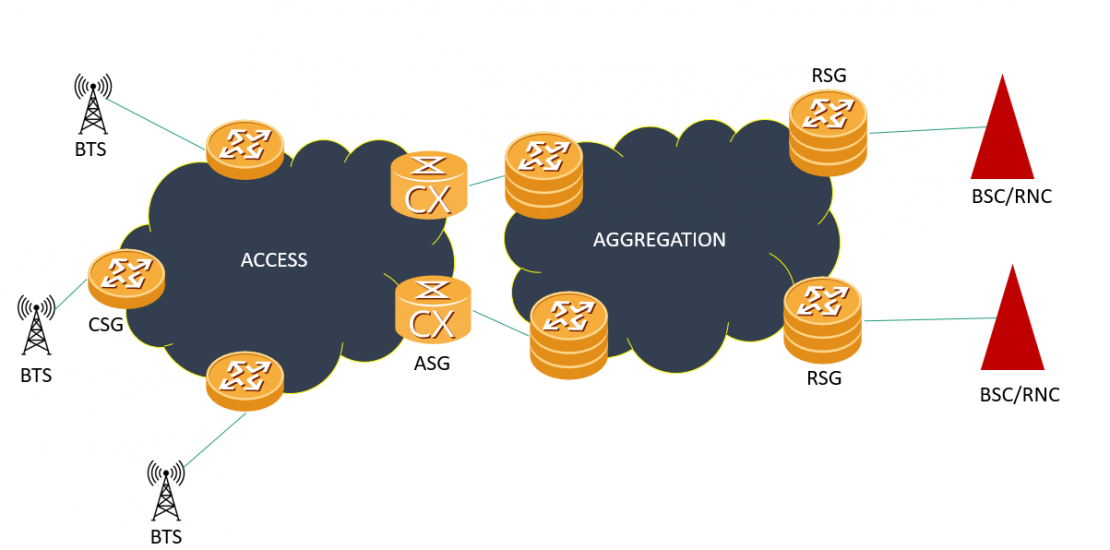
Radio Access Network(RAN) is the transport network deployed between the base stations (BTSs/NodeBs/eNodeBs/gNBs) and base station controllers (BSCs/RNCs/EPC nodes/5GC nodes). It can also be referred to as a Base station backhaul network.
IPRAN network is the Radio Access Network (2G, 3G, 4G, or 5G) which uses IP as the transport layer technology. It is an integrated router/switch solution customized for IP-based base station backhaul scenarios. This replaces the traditional technologies like TDM/SDH/Microwave etc. IPRAN offers carriers a flexible, reliable, and cost-effective base station backhaul network solution that is easy to deploy, manage, and evolve.
There are three layers for access networks:
1) Access Layer. Connects to the base stations, the nodes in this layer are referred to as CSGs( Cell Site Gateway)
2) Aggregation layer: Aggregates the access traffic and connects the access to the core, nodes in this layer are referred to as ASGs(Aggregation Site Gateway).
3) Core layer: Connected to the controllers and the core network, nodes in this layer are referred to as RSGs(Radio Site Gateway)
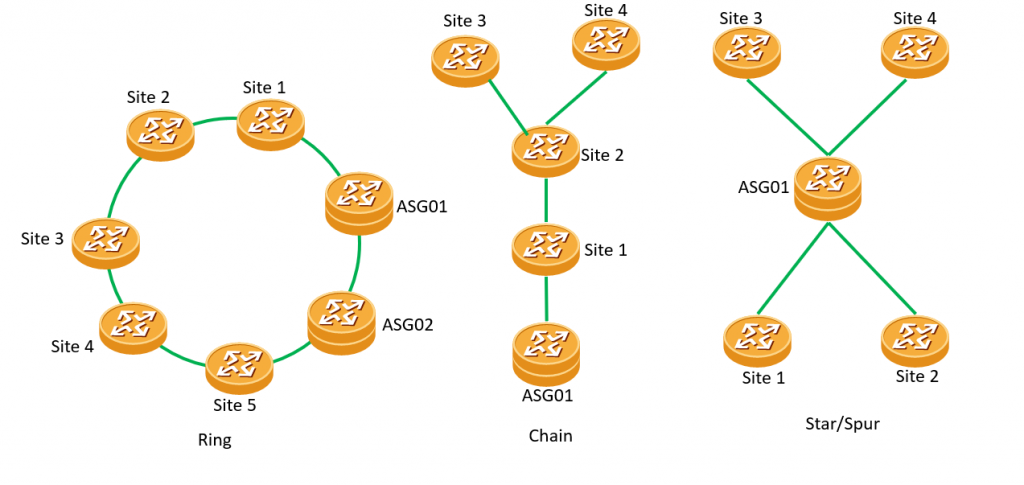
IPRAN network can be implemented in different setups. The most common setups are ring, chain, and star. Ring topologies are preferred by ISPs because they provide redundant paths for access traffic in case of link or node failures in the network. Chain and Star are not preferred because they are single points of failure.
Protocol Selection for IPRAN. Different routing and switching protocols are configured on IPRAN to ensure connecting and forwarding of traffic from BTS to the controllers.
- IGP(Interior Gateway Protocol): This is run within an AS and ensures connectivity within an AS. The most common IGPs used in ISP networks are OSPF, IS-IS, and EIGRP.
- BGP(Border Gateway Protocol). BGP comes in two flavors, Interior Border Gateway Protocol (IBGP) and Exterior Border Gateway Protocol(EBGP). IBGP is implemented within and is used to exchange service routers between CSGs, ASGs, and RSGs. EBGP is implemented between two ASes and used to exchange routes between the two ASes.
- MPLS( Multi-Protocol Label Switching): Layer 2.5 technology that forwards traffic based on Labels instead of network addresses.
- LDP(Label Distribution Protocol): Used to distribute MPLS labels in the MPLS network.
- RSVP-TE: Used for traffic engineering
Service Separation on IPRAN. The IPRAN network is used to carry different services with different requirements. These services include 2G,3G,4G and 5G. The DCN for sites is always carried on IPRAN. These services are separated using VPN instances or VRFs ( Virtual Routing and Forwarding). Each VRF is assigned different RDs and RTs to control route import and export.
Quality of Service for IPRAN. To meet the requirements for services that require special treatment like voice and video and other critical services, QOS should be well implemented in the IPRAN network. Traffic classification and marking should be done at the network ingress points. Queuing, traffic shaping, and policing should be implemented end to end.
3,043 Comments
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Many thanks for this interesting topic, it would be great if you add more details about the Needed configuration, protocols used at each level , the Traffic flow from radio nodes to RNC/MME via IPRAN
Sure Stan. Will be sharing another article on protocols and many more details on IPRAN. Thanks for your feedback.
Cool stuff. Always a great pleasure, learning new things everyday. Keep sharing