Implementing Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) manual mode on Huawei routers.
- July 28, 2024
- Posted by: James Majani
- Categories: Huawei, Networking
Basic Concepts.
IPSec is a suite of protocols and services that provide security for IP networks. It is a widely used Virtual Private Network (VPN) technology. IP packets lack effective security mechanisms and may be forged, stolen, or tampered with when being transmitted on a public network, such as the Internet. To solve this problem, the communicating parties establish an IPsec tunnel for encrypted transmission of IP packets. This ensures secure transmission of IP packets on an insecure network, such as the Internet.
IPSec has several standards:
IP Security Protocol
o Authentication Header (AH)
o Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
Triple DES (3DES)
Diffie-Hellman (D-H)
Message Digest 5 (MD5)
Secure Hash Algorithm-1 (SHA-1)
Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman (RSA) Signatures
Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
Certificate Authorities (CAs
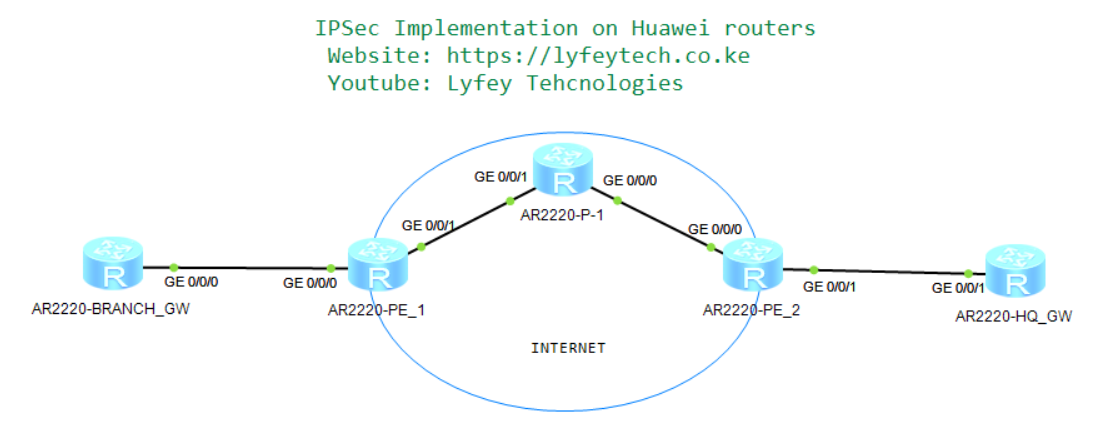
Networking Description.
As shown in our topology, HQ router and Branch router, are gateways of the enterprise headquarters and branch. The service provider has allocated a public network IP address to each gateway and the gateways can communicate with each other.
The enterprise requires a simple cost-effective mechanism to implement communication between the headquarters and branches through Internet. IPSec tunnels can be established between the headquarters and branches to meet this requirement.
In this environment, BGP is used in the backbone network, between Branch1 and ISP router (PE_1) BGP is used to exchange Public IPS of the gateways across the Internet. Between HQ router and Internet router (R5) OSPF protocol is configured to create routing entries. IPSec is deployed between Branch and HQ for secure transmission of data over the internet between the two sites.
Step 1: Basic configurations.
*******************************************AR222_BRANCH_GW
system-view
sysname AR222_BRANCH_GW
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.1.0.2 255.255.255.252
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface LoopBack1
ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
*******************************************AR222_PE_1
system-view
system-view
sysname AR222_PE_1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.252
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.252
*******************************************AR222_P_1
system-view
sysname AR222_P_1
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.252
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.252
*******************************************AR222_PE_2
system-view
sysname AR222_PE_2
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.252
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 10.3.0.1 255.255.255.252
*******************************************AR222_HQ_GW
system-view
sysname AR222_HQ_GW
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 10.3.0.2 255.255.255.252
ipsec policy P1
#
interface LoopBack0
ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
#
interface LoopBack1
ip address 192.168.33.1 255.255.255.0
Step 2: Configure routing protocols for route exchange.
*******************************************AR222_BRANCH_GW
bgp 100
peer 10.1.0.1 as-number 300
#
ipv4-family unicast
undo synchronization
network 10.1.0.0 255.255.255.252
network 192.168.1.0
network 192.168.11.0
peer 10.1.0.1 enable
*******************************************AR222_PE_1
bgp 300
peer 10.1.0.2 as-number 100
peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 400
#
ipv4-family unicast
undo synchronization
import-route direct
peer 10.1.0.2 enable
peer 172.16.1.2 enable
*******************************************AR222_P_1
bgp 400
peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 300
peer 172.16.2.1 as-number 500
#
ipv4-family unicast
undo synchronization
import-route direct
peer 172.16.1.1 enable
peer 172.16.2.1 enable
*******************************************AR222_PE_2
bgp 500
peer 172.16.2.2 as-number 400
#
ipv4-family unicast
undo synchronization
import-route direct
import-route ospf 1
peer 172.16.2.2 enable
#
ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1
import-route bgp
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.3.0.0 0.0.0.3
*******************************************AR222_HQ_GW
ospf 1
area 0.0.0.0
network 10.3.0.0 0.0.0.3
network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.33.0 0.0.0.255
Step 3: Create access lists to match interesting traffic.
*******************************************AR222_BRANCH_GW
acl number 3001
rule 5 permit ip source 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 destination 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255
*******************************************AR222_HQ_GW
acl number 3001
rule 5 permit ip source 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 destination 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255Step 4: Start IPSec VPN configuration by first creating IPSec Proposal at the GWs.
*******************************************AR222_BRANCH_GW
ipsec proposal PRP1
esp authentication-algorithm sha2-256
esp encryption-algorithm aes-128
*******************************************AR222_HQ_GW
ipsec proposal PRP1
esp authentication-algorithm sha2-256
esp encryption-algorithm aes-128Authentication-algorithm and encryption-algorithm must match on local and remote site.
Step 5: Cofigure IPSec policy and apply the policy to the relevant interfaces.
*******************************************AR222_BRANCH_GW
ipsec policy P1 10 manual
security acl 3001
proposal PRP1
tunnel local 10.1.0.2
tunnel remote 10.3.0.2
sa spi inbound esp 123456
sa string-key inbound esp cipher huawei@123
sa spi outbound esp 654321
sa string-key outbound esp cipher huawei@123
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ipsec policy P1
*******************************************AR222_HQ_GW
ipsec policy P1 10 manual
security acl 3001
proposal PRP1
tunnel local 10.3.0.2
tunnel remote 10.1.0.2
sa spi inbound esp 654321
sa string-key inbound esp cipher huawei@123
sa spi outbound esp 123456
sa string-key outbound esp cipher huawei@123
#
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ipsec policy P1IPSec can be configured in two ways: manual mode and ISAKMP mode. In manual mode, you have to manually set SA parameters like the SPI and the key. In ISAKMP mode, they are determined by the IKE negotiation. In this case we used manual mode.
Step 6: Results verification.
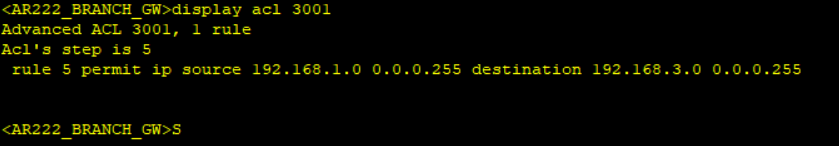
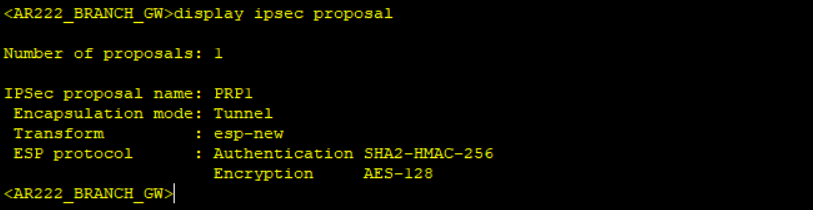
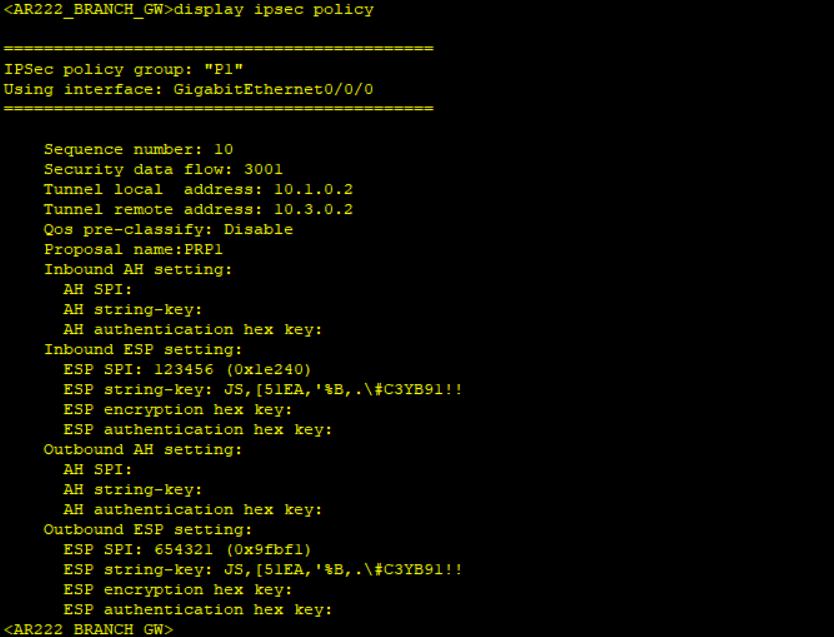
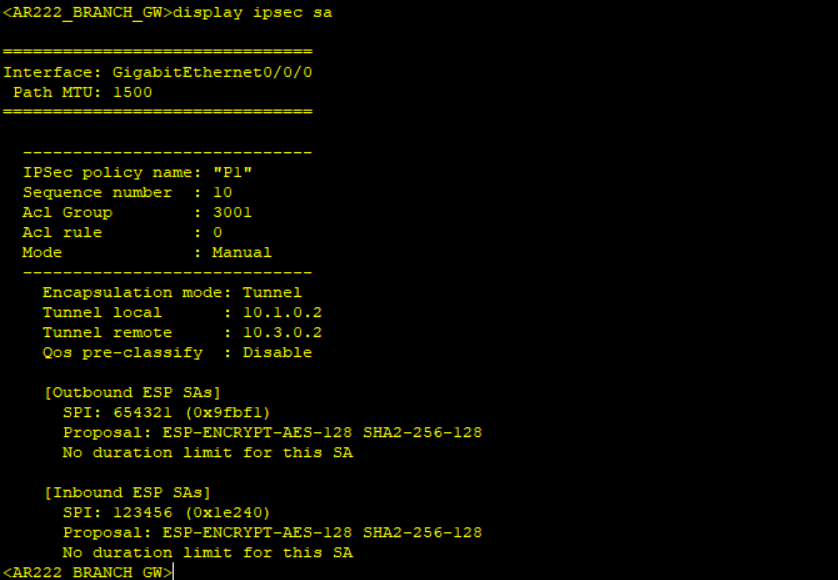
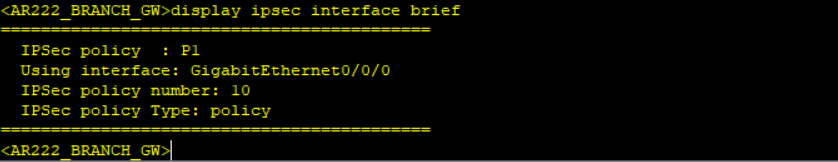
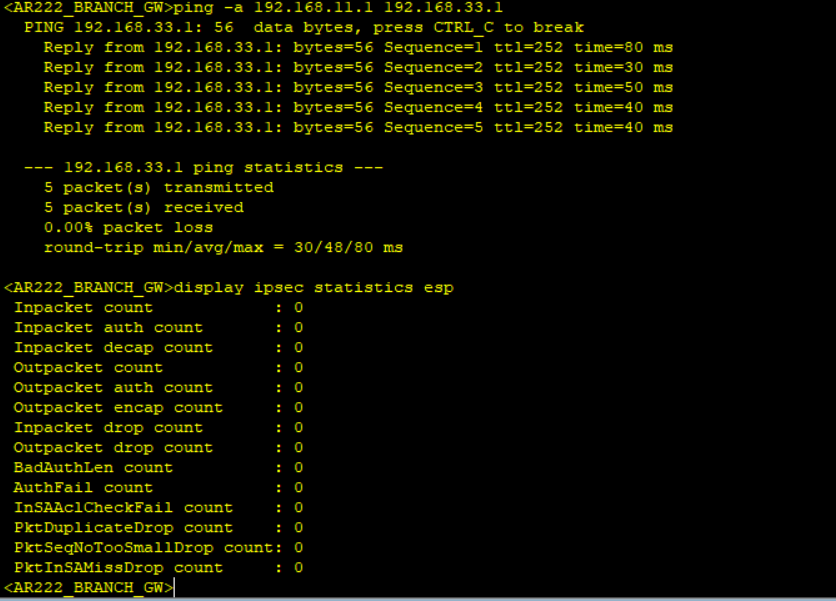
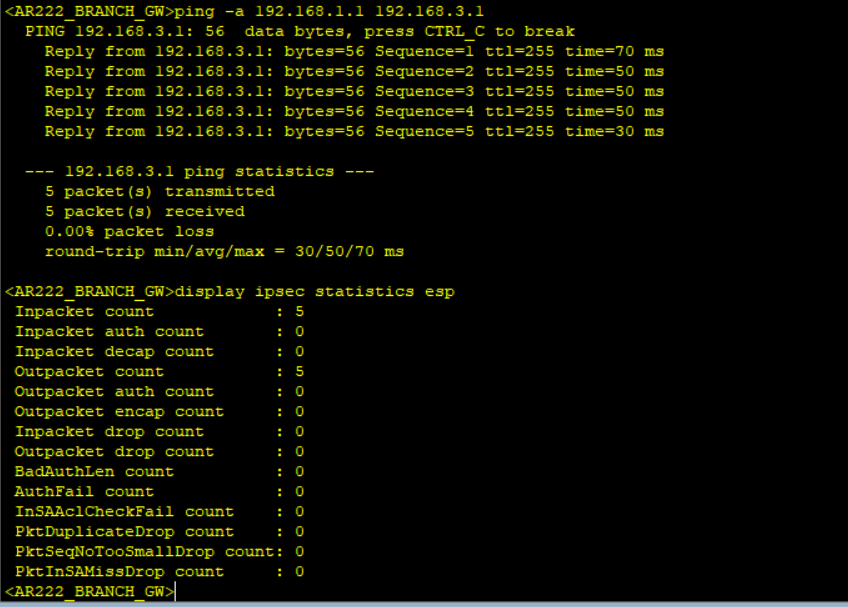
Notice no packet count when displaying IPSec statistics after simulating traffic not matching interesting traffic and packet count when interesting traffic matching the created ACL is simulated.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
